Optimising Moisture Management in Bulk Solids
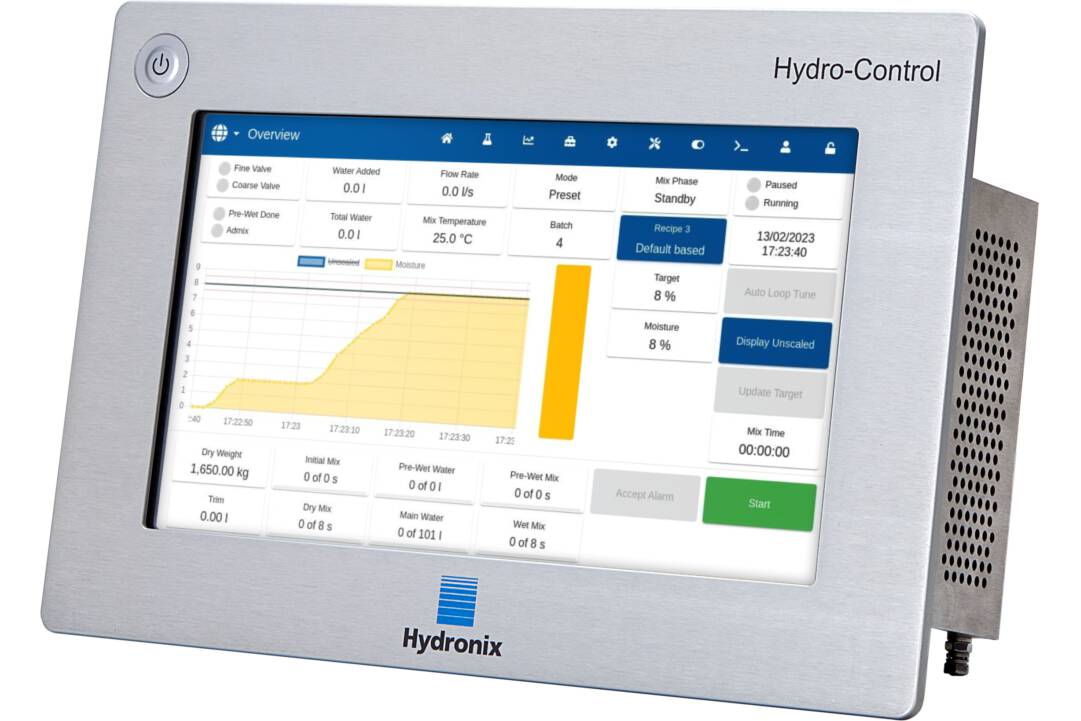
Modern industrial processing relies on automation to maintain consistent quality. While moisture is a critical variable in production, manual testing is often too slow for real-time control. Inline sensors provide the necessary responsiveness, but the choice between absolute and relative values dictates the efficiency of the system.
Differentiating Absolute and Relative Values
Absolute moisture measurement represents the literal percentage of water in a material, requiring extensive laboratory testing and precise calibration. In contrast, relative values focus on the stability and repeatability of the sensor signal. This approach allows a controller to react to whether a material is wetter or drier than a set target.
The Advantage of Repeatable Control Loops
For automated processes like material conditioning or drying, absolute values are less critical than consistent feedback. A repeatable relative measurement allows the system to adjust water addition or drying times proactively. This method ensures predictable material behavior and high-quality output without the burden of constant recalibration.
Digital Sensors and Machine Learning
Digital microwave sensors provide the stable signals required for this control strategy, remaining unaffected by changes in particle size or dust levels. Integrating machine learning further enhances the process by analyzing historical data to predict moisture changes. This technology minimizes manual intervention and automatically compensates for raw material variability.
Strategic Value of Relative Measurement
- Simplifies sensor setup by removing the need for complex calibration.
- Enhances real-time responsiveness in automated control loops.
- Reduces energy consumption through optimized drying and mixing cycles.
- Minimizes production interruptions caused by raw material fluctuations.
- Frees operators to focus on high-value tasks instead of manual adjustments.